Appendix A
Memories and busses
A.1 ROM memory
A.1.2 Operating principle
Example of a 16x4 ROM component (containing the samples of a sine wave):
An example of ROM application: a sine wave generator
A.1.3 Internal architecture
PLA (Programmable Logic Array):
ROM (with content yet to be programmed):
ROM (programmed as a math function):
A.2 RAM memory
A.2.2 Internal architecture
A parallel register:
RAM memory example (4 locations of 4 bits each):
RAM memory example (64 locations of 8 bits each):
A.3 Bidirectional bus connections
Four data sources and a multiplexer:
Four data sources and a multiplexer (bus version):
A.3.1 Tri-state buffers
Four data sources and a connection based on tri-state buffers:
A.3.2 Tri-state buffers and busses
A component that includes eight tri-state buffers::
Four data sources and a connection based on tri-state buffers (bus version):
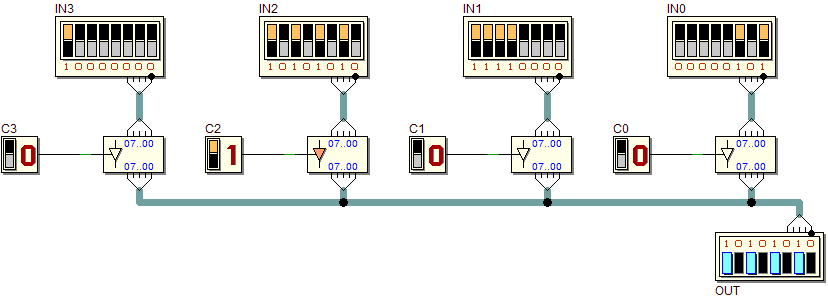
Four data sources and a connection based on tri-state buffers (selection by address):
Bidirectional bus connection of four generic "slave" units to a "master" controller:
Bi-directional tri-state buffer:
A.3.3 Tri-state memories
4Kx8 ROM component with tri-state bus, and its equivalent network.
(Note: the circuit also includes the components needed for the simulation).
4Kx8 RAM component with bidirectional tri-state bus and its equivalent network.
(Note: the circuit also includes the components needed for the simulation).
A. Errata Corrige
None